Gas fermentation: using CO₂ as a valuable resource
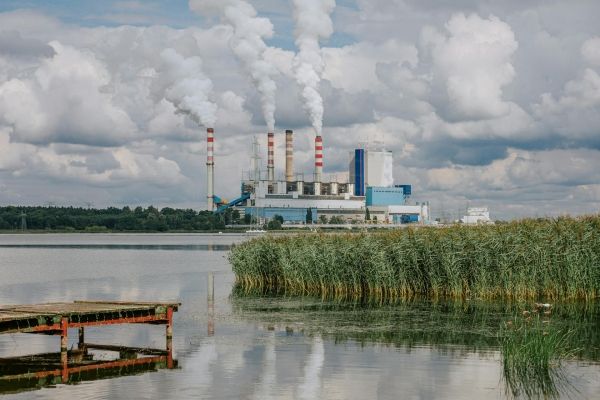
Thanks to gas fermentation, you can extract carbon-rich gases (such as CO₂) from the atmosphere and turn them into high-quality products for the chemical industry. These products are the perfect alternative to fossil chemicals derived from petroleum and natural gas.
A sustainable fermentation process through bioconversion
Fermentation is an ancient process that’s used for the most diverse purposes. From cosmetics to pharmaceutical products and biomaterials: these days, many things are produced by fermentation.
Many traditional fermentation processes use sugars or organic materials as a resource. Gas fermentation, on the other hand, relies on the principle of bioconversion. It converts micro-organisms, that feed on carbon-rich gases like CO₂ and methane, into platform chemicals, fuels, polymers, etc.
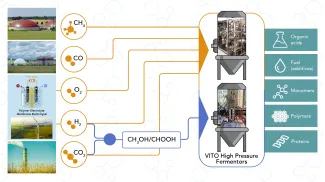
The benefits of gas fermentation
Biological processes have a number of benefits over chemo-catalytic or thermochemical ones for the conversion of these carbon-rich gases:
- Contribution to the climate goals by repurposing carbon-rich gases
- Higher conversion efficiency
- Higher product specificity or selectivity
- Lower sensitivity to variations in gas composition
- Higher tolerance to impurities that poison inorganic catalysts
Gas fermentation is on the rise
For certain applications, gas fermentation has already grown to a semi-commercial scale. VITO conducts research into this technology across the board: from the scientific area to the technical and economic ones.
Meer weten over gasfermentatie?
We’re happy to give you more information or look into the ways gas fermentation can be used in your processes.
FAQ: gas fermentation
VITO’s equipment and expertise in gas fermentation could be interesting for:
- Companies that want to valorise their carbon-rich gas emissions
- Companies that want to test their (genetically modified) micro-organism in a state-of-the-art gas fermentor
- Technology developers or suppliers
- Companies looking for alternative resources.
VITO offers:
- The necessary equipment and knowledge of gas fermentation, including bioprocess design, engineering and optimisation.
- Know-how of process intensification, more specifically the integration of bioprocesses with membrane separation technology for the retention of biocatalysts of in-situ product removal.
- Evaluation of the technical and economic manageability of different applications in proof-of-concept and validation studies.



