Medical implants have to comply with strict quality requirements. Various ceramic and metal structures are suitable for this. We provide advice about the choice of material and develop the necessary design processes.
MooV is an optimization service that improves the efficiency of your supply chain and reduces its cost. MooV finds the best supply chain configuration meeting the specific requirements and ambitions of your business.
Maximising the valorisation of your waste streams requires good separation techniques. You can count on our expertise for this. We have developed technologies for separating materials based on their physical properties. This allows us to help you get the most out of your waste stream.
We have developed innovative plasma technology to permanently modify the surface of materials at normal atmospheric pressure. The desired surface properties are obtained by a range of plasma coating systems.
We employ wash coating techniques to deposit active powders (slurry) onto structured supports. A well-known example is the production of catalysts for diesel exhausts by wash coating ceramic honeycombs. We employ the same method to apply catalysts onto structured supports for chemical conversions.
GOAL is VITO’s specialist lab for organic and inorganic chemical analysis. Our lab rarely performs standard measurements, instead it offers custom solutions to its customers.
Drastic improvements are targeted by redesigning existing production schemes into more efficient ones. This often involves integrating a separation step during the (enzymatic) reaction resulting in a more efficient and economical process. Different strategies to address potential drawbacks of enzymatic processes such as substrate and/or product inhibition, unfavourable equilibria, unwanted product (bio)transformation, can be investigated and implemented.
Biotechnology is one of the key enabling technologies that will allow the sustainable production of fuels, chemicals and materials. Despite the progress in genetic and metabolic engineering, several bio-based processes are still plagued by limited product titers and volumetric productivities or suffer from side reactions decreasing the yield of the process. That's why technological breakthroughs are needed to intensify the processes and reduce the consumption of energy and resources. Among them is the combination of bioconversion processes with separation technology. VITO often applies membrane technology because it is modular, may introduce selectivity, operates under mild environmental conditions and can easily be integrated with bioprocesses.
Gas fermentation is a technology that uses micro-organisms to convert gaseous feedstocks such as carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), syngas, methane (CH4), or biogas, into platform chemicals, fuels, polymers, etc.
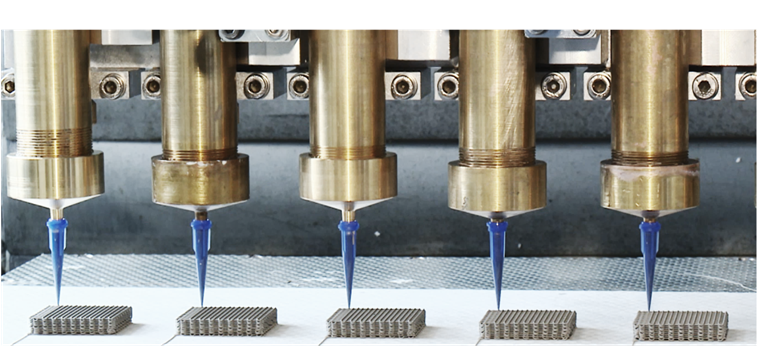
3DPRIME
3D micro-extrusion
With 3D micro-extrusion, high-quality functional components such as catalysts, sorbents, heat exchangers and electrodes can be produced via 3D printing, which is crucial for making the sector more sustainable. VITO has already successfully tested this technology at laboratory scale. To validate the technology in industrial conditions, scaling up to pilot scale is necessary.
Unique worldwide
This new pilot line is unique in the world and offers companies the opportunity to test the technology in an industrial environment. The pilot line strengthens VITO's position as a knowledge centre in 3D printing and promotes co-creation and innovation in Flanders and beyond. The facility can produce up to one tonne per month of functional components in an automated, (semi-)continuous process, a crucial step for market introduction.
Europees Fonds voor Regionale Ontwikkeling
With this investment, VITO is taking an important step in increasing the sustainability of the chemical and energy sectors, and offering the industry new opportunities to implement innovative technologies faster and more efficiently.
The development of the pilot plant in the 3DPRIME project is financially supported by the Europees Fonds voor Regionale Ontwikkeling (EFRO) aand the Fonds voor Innoveren en Ondernemen (FIO).
Transforming groundbreaking technologies into a scalable business requires more than just a great idea or scientific innovation. It demands strategic foresight, the right partnerships, and a deep understanding of the complex landscape of growth and investment. Precisely that is what (co)founders of deep tech start-ups can learn in this new learning track ‘Scaling with Impact’ developed by Antwerp Management School, the University of Antwerp and VITO. They brought together their expertise in working with early and later-stage, innovative and technology-driven start-ups to empower their growth and help them scale up.
VITO is taking an important step towards the sustainability of the chemical and energy sectors. The construction of an advanced 3D printing pilot line responds to the growing demand from industry for innovative components under industrially relevant conditions. This project is supported by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) and the Innovation and Enterprise Fund (FIO).
A lot of activity at EnergyVille, as this month the construction work began on a thermal network of the so-called fifth generation at Thor Park in Genk. This network will allow the various buildings within the Thor Science Park – both existing and future buildings – to be sustainably heated and cooled, based on shallow geothermal energy. It is one of the first networks of its kind in Belgium and is built in a modular way, allowing for quick expansion and scaling. In short, a crucial cornerstone in EnergyVille’s (and its partners KU Leuven, VITO, imec, and UHasselt) research into a more sustainable energy supply.
Start-up CIRCULIFE provides circular management of companies' electronic devices, through which they aim to minimise the e-waste and maximise the (re)use of devices, parts and raw materials. With their innovative tool, they act as the bridge between manufacturers, companies and repairers, creating added value for each party in the chain. Thus, CIRCULIFE's participation in VITO4STARTERS in March this year did not go unnoticed; they became runner-up and so began the collaboration with VITO.
Genk, 25 March 2024 – Green hydrogen is crucial if the energy transition is to succeed. After all, hydrogen is needed for the greening of so-called hard-to-abate sectors such as heavy industry (steel, cement, chemicals), shipping, etc. For years, the EnergyVille partners, VITO, imec and UHasselt have been dedicating research to hydrogen. Flanders, too, worked out a hydrogen vision and, in the Flemish “Vlaamse Veerkracht” plan, earmarks investments for innovation in hydrogen. Today, the latest hydrogen infrastructure is being presented in Genk. The Flemish government invested 4.5 million euros for this through the Flemish relaunch plan “Vlaamse Veerkracht”.
Things are moving fast in the world of batteries and the countless applications they power. In order to provide the best possible answers to specific questions from manufacturers, VITO/EnergyVille offers a particularly wide and varied range of battery tests and corresponding expert advice. ‘In recent years, we have seen a strong differentiation in the market, and we take that into account.’
S+T+ARTS4WATERII is excited to announce the Call for Artists for the second edition of the S+T+ARTS Residency Programme, which is dedicated to water sustainability and innovation at the nexus of science, technology, and arts. This time, the programme has a specific focus on the environmental challenges of ports, port cities, coastal areas, and waterways.
VITO is the coordinator of S+T+ARTS4WATERII. The other partners of the consortium are TBA21 (Spain and Italy), Camargo foundation (France), WAAG Futurelab (the Netherlands), GLUON (Belgium), OGR Torino (Italy), ADAPT Research Centre (Dublin), Klima Biennale Wien (Austria), Drugo More (Croatia) and PiNA (Slovenia).
The Blue Cluster is spearheading sustainable and innovative development within the blue economy. Defined as the “sustainable use of ocean resources to benefit economies, livelihoods, and ocean ecosystem health,” the blue economy encompasses a wide range of activities including maritime shipping, fishing and aquaculture, coastal tourism, renewable energy, water desalination, undersea cabling, marine genetic resources, and biotechnology.
PEFCR4Space: a sustainable future for the space sector
Today, there is no common agreement on space sector-specific rules for life cycle-based assessment shared along the value chain, nor on reference systems for space systems, space projects or space programmes. Therefore, a specific PEFCR for the space sector will be developed to promote the manufacturing and deployment of environmentally sound and sustainable space activities and products, and to enable space actors to provide and access reliable information in a transparent manner.
This work will follow the EU recommended Product Environmental Footprint (PEF) and Organisation Environmental Footprint (OEF) methodologies as set out in EU Commission Recommendation 2021/2279.
The role of PEFCR in the space sector
Standardising environmental impact assessments
Over the last decade, several actors in the European space industry have been working on the life cycle environmental impact assessment of space activities. The development of a PEFCR for the space sector provides a consistent approach to assessing the environmental impacts of space activities, which is crucial for comparing the performance of complex supply chains and technologies. A space PEFCR will provide companies with a systematic method to assess the environmental footprint of their products, promote informed decision making and foster a market that prioritises sustainability.
Project overview
The Space PEFCR initiative focuses on the development of PEFCRs and Environmental Footprint (EF)-compliant datasets for the EU space sector, enabling tailored environmental assessments that address sector-specific needs.
Key objectives:
- Develop space sector specific PEFCRs based on the EU Product Environmental Footprint (PEF) method.
- Define and acquire EF-compliant data sets to ensure reliability and comparability.
- Engage stakeholders to promote green and sustainable products and services.
Stakeholder engagement and outreach
The engagement of industry representatives and experts will be crucial for the development of a space PEFCR and for the successful implementation of this project. Broad stakeholder engagement will ensure the involvement of field experts in the technical development of the PEFCR, in supporting studies and dataset creation to reflect stakeholder needs, and finally in broad dissemination activities to inform about the benefits of the space PEFCR.
The role of VITO and our partners
The PEFCR Space project, commissioned by the European Commision (DG DEFIS), is implemented by an external consortium coordinated by VITO, together with other PEFCR and technical experts from PRé Sustainability, Ecomatters, Ecoinnovazione, Glasgow Caledonian University, and Novaspace.